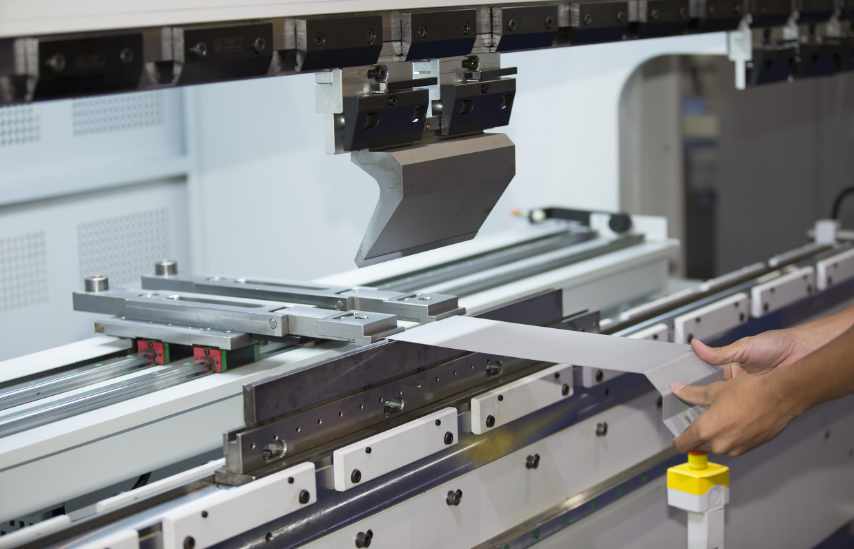
Did you know that metal-forming processes are at the heart of many industries? From the cars we drive to the buildings we inhabit, metal forming is a fundamental manufacturing technique that enables the creation of complex and durable metal components.
In this article, we will uncover the metal forming processes, exploring the techniques, applications, and materials involved.
Types Of Metal Forming Processes
From forging to rolling, stamping, extrusion and drawing, each process involves unique techniques and tools to shape metal into desired forms. Understanding these processes will give you a better understanding of how metal is manipulated and formed in various industries.
Forging
This process involves heating metal and then applying compressive forces to shape it. It is frequently used to create parts with high strength and durability, such as automotive components and tools.
Rolling
In this process, metal is passed through a pair of rollers to reduce its thickness or alter its shape. Rolling is commonly used in the production of sheet metal, plates, and structural components.
Stamping
Stamping is a process that uses a die to cut or shape metal into a specific form. Typically used in various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and consumer goods.
Drawing
Drawing is a process where metal is pulled through a die to reduce its diameter and increase its length. It is commonly used in the production of wires, rods, and tubes.
Extrusion
This process involves forcing metal through a die to create complex cross-sectional shapes. It is commonly used in the production of pipes, tubes, and profiles with uniform dimensions.
Machinery Used In Metal Forming
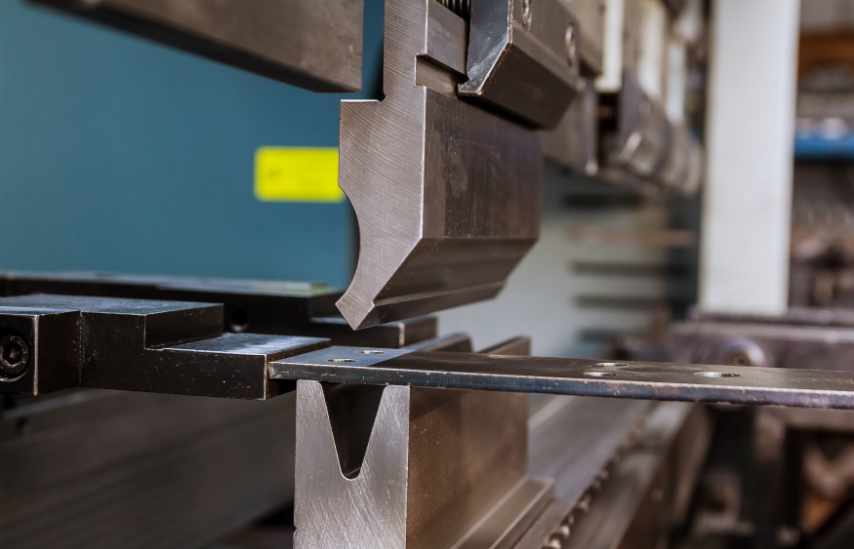
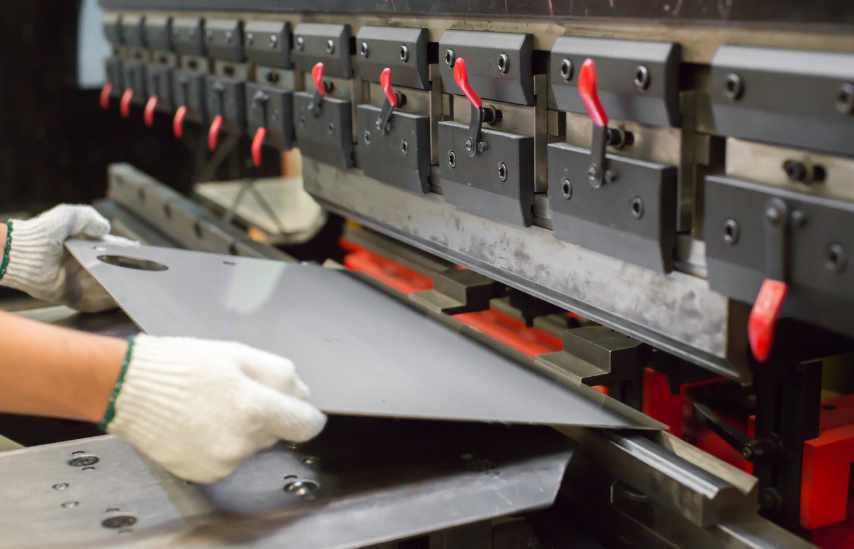
Press Brakes
A press brake is a machine tool used in sheet metal fabrication to bend and fold sheet metal into various shapes and angles. It works by pressing a punch into the sheet metal which is positioned on a die, creating the desired bend. The punch and die combination determine the angle and shape of the bend. Press brakes are essential for creating precise bends in sheet metal for a wide range of applications in industries such as automotive, aerospace, construction, and more.
Press brakes come in various sizes and configurations, but they typically consist of the following key components:
Frame
The frame provides the structure and support for the press brake. It is usually made of heavy-duty steel to withstand the high forces generated during bending operations.
Bed
The bed is the flat surface where the lower die is mounted. It provides support for the sheet metal being bent and ensures accurate bending.
Ram
The ram is the moving part of the press brake that carries the upper die. It moves vertically to apply pressure to the sheet metal and form the bend.
Upper and Lower Die
The upper die, also known as the punch, and the lower die, also known as the die block or V-die, work together to shape the sheet metal into the desired bend. The upper die attaches to the ram, while the lower die is mounted on the bed.
Back Gauge
The back gauge is a device used to position the sheet metal accurately before bending. It helps ensure consistent bending dimensions and repeatability.
Hydraulic System
Most modern press brakes use hydraulic systems to generate the force needed for bending. Hydraulic cylinders apply pressure to the ram, which in turn applies force to the sheet metal.
Control System
Press brakes are often equipped with computerised control systems that allow operators to program bending sequences, adjust bending parameters such as angle and bend length, and monitor the bending process for accuracy and safety.
Press brakes can be categorised based on their bending force capacity, bending length, and control system sophistication. They are versatile machines capable of bending various materials, including steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, into complex shapes and angles with high precision.
CNC Punches
CNC punches with form tool capabilities are used to create bends in sheet metal using a different method compared to press brakes. Here's how it works:
Programming
The first step involves programming the CNC machine with the desired bend specifications. This includes the angle of the bend, the length of the bend, and any other parameters necessary for the specific application.
Tooling
A form tool is selected based on the desired bend shape and angle. Form tools come in various shapes and sizes to accommodate different bending requirements.
Material Setup
The sheet metal to be bent is securely clamped onto the CNC punch machine's work table.
Tooling Setup
The form tool is mounted onto the CNC punch machine's tool holder. The machine's control system ensures precise positioning of the tool relative to the sheet metal.
Bending Process
The CNC punch machine moves the form tool into contact with the sheet metal at the programmed location. The tool exerts force on the material, causing it to deform and create the desired bend shape. The CNC control system ensures accurate positioning and control of the bending process.
Repeat
Depending on the complexity of the part being fabricated, the CNC punch machine may perform multiple bending operations using different form tools to achieve the final part shape.
Compared to press brakes, CNC punches with form tool capabilities offer advantages such as faster setup times, higher throughput, and the ability to create complex bend shapes. They are commonly used in sheet metal fabrication for producing parts with bends, flanges, and other features in a single operation.
Which Industries Use Metal Forming?
Metal forming is a widely utilised manufacturing process in various industries. It plays a crucial role in shaping and transforming metal materials to meet the specific needs of different applications. Several industries rely on metal forming to create a wide range of products.
Automotive Sector
Metal forming is driven by the need for lightweight design solutions and automated driving, as well as the demand for reduced car weight and increased fuel economy.
Aerospace Industry
This industry utilises metal forming to create structural elements, cladding panels, and engine parts. These components, crucial for their high precision and intricate shapes, are fundamental to the sector.
Construction Industry
The construction industry employs metal forming to fabricate structural elements and building components. This process guarantees strength, longevity, and the ability to tailor features to specific construction needs.
Consumer Goods Industry
Relies on metal forming for products such as pots, cans, and coatings, which require standardised quality and specific size and fit requirements.
Materials Used In Metal Forming
One crucial aspect of metal forming is the selection of materials used in the process. The choice of materials depends on the method and desired properties of the metal.
Commonly used metals in metal forming include aluminium, steel, brass, copper, tin, lead, magnesium, zinc, and titanium.
Aluminium
Its excellent strength-to-weight ratio makes it extensively used in sheet metal forming.
Aluminium is a preferred choice for its ability to meet specific size and fit requirements in consumer goods.
Copper
Copper, known for its corrosion resistance, makes it suitable for applications in harsh environments. Its malleability allows for easy shaping and forming, making it a versatile material in metal fabrication.
Steel
Steel is a versatile metal that's widely used in various industries for its strength and durability. It's composed of iron and carbon, which determine its hardness and tensile strength.
There are different types of steel, including carbon steel and stainless steel. Carbon steel is known for its versatility, durability, and malleability, while stainless steel is corrosion-resistant and has a silver mirror coating.
Factors to Consider in Metal Forming Processes
Material Suitability
When considering metal forming processes, it's crucial to assess the suitability of materials for the desired shape and properties. The material you choose will greatly impact your metal-forming process.
You need to consider factors such as the material's strength, ductility, and ability to withstand the forming process. For example, if you're looking to create a complex shape, you may need a material that's highly malleable and can be easily shaped without cracking or breaking.
On the other hand, if you're aiming for a part that requires high strength, you'll need a material with excellent strength properties.
Cost- Effectiveness
These processes, such as roll forming, bending, extrusion, and forging, can offer significant cost advantages.
Bending, for example, is often used to create complex shapes from sheet metal and can be done by hand or using a machine.
Press braking, stamping, and forging are also cost-effective options for producing high volumes of parts with consistent designs.
Production Efficiency
Metal forming processes like roll forming, bending, and stamping provide high production efficiency, enabling quick and effective manufacturing. These methods ensure consistent quality, precise dimensions, and minimise waste, enhancing productivity. Advanced technologies and automation further boost production rates, maintain tight tolerances and allow for complex shapes.
Quality of Final Product
The quality of the final product is crucial in metal forming processes as it determines the performance and durability of the metal parts.
This depends on several factors including, accuracy and precision of the metal forming process, choice of materials and surface finish.
Lastly, the skill and experience of the operators involved in the forming process shouldn't be overlooked, as their expertise can significantly impact the outcome of the process. Here at Wrekin Sheetmetal, our upskilling program means that our team are constantly improving their skills. Our commitment to upskilling not only benefits our employees but also enhances the overall productivity and efficiency of our organisation.
In conclusion, metal forming processes play a crucial role in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and construction.
These processes, including rolling, extrusion, stamping, and sheet metal forming, allow for the shaping and manipulation of metals into different forms. The versatility and wide range of applications make metal forming an essential manufacturing process in today's world.
Take a look at our metal-forming page to find out more about our capabilities.

How can we help?
With over 17+ years of knowledge and experience, we’re confident we can offer a flexible solution beneficial to both parties, get in touch with us today.