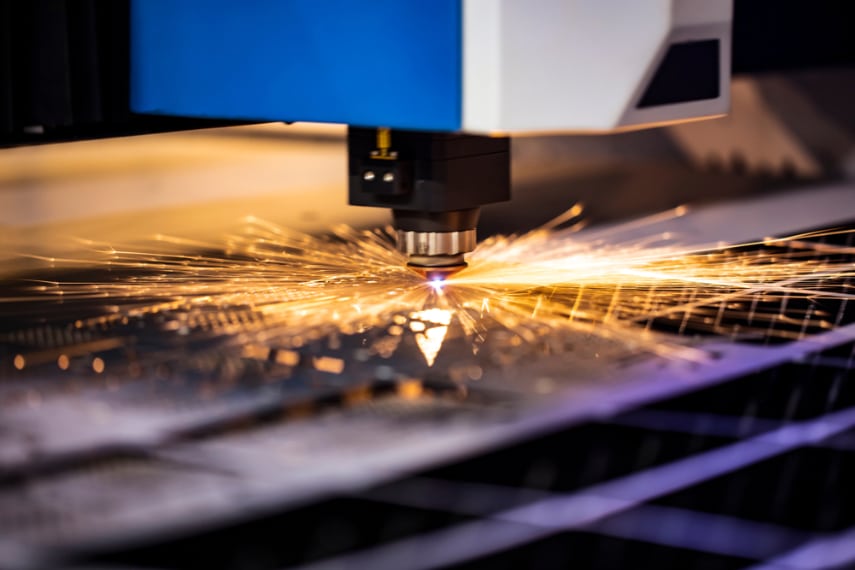
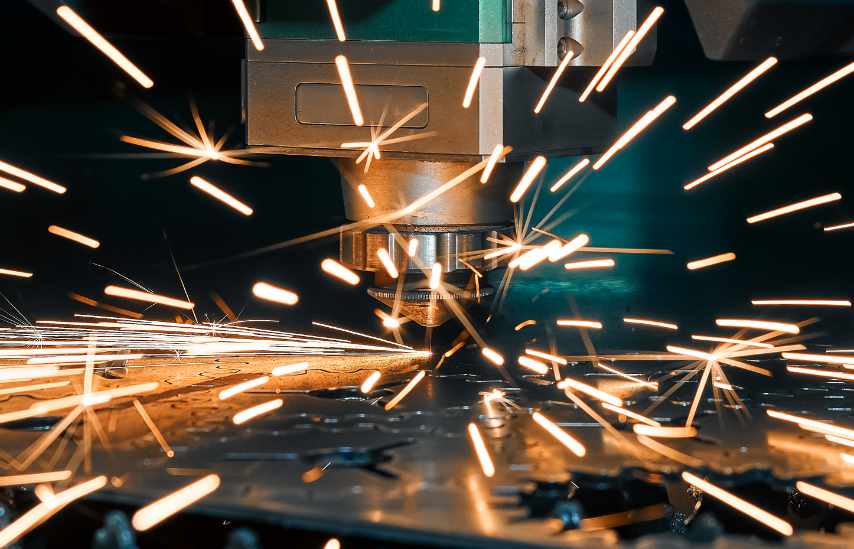
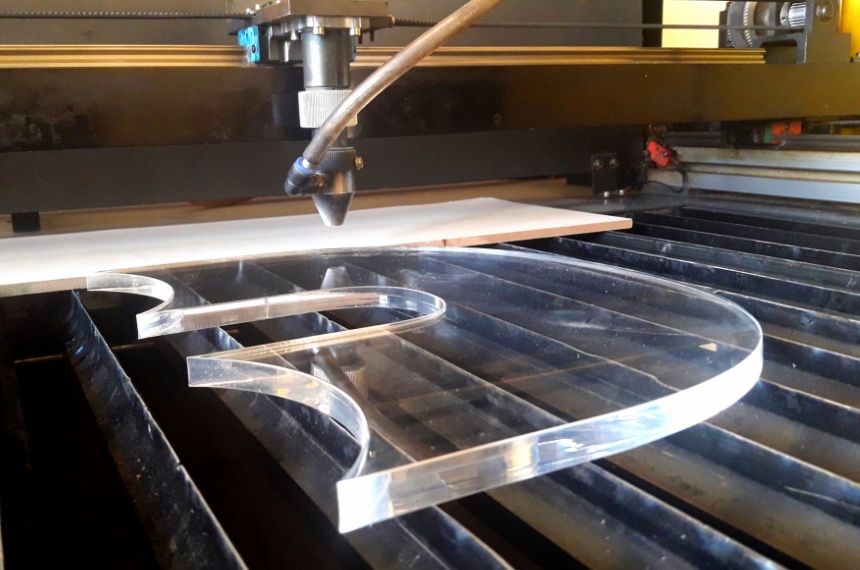
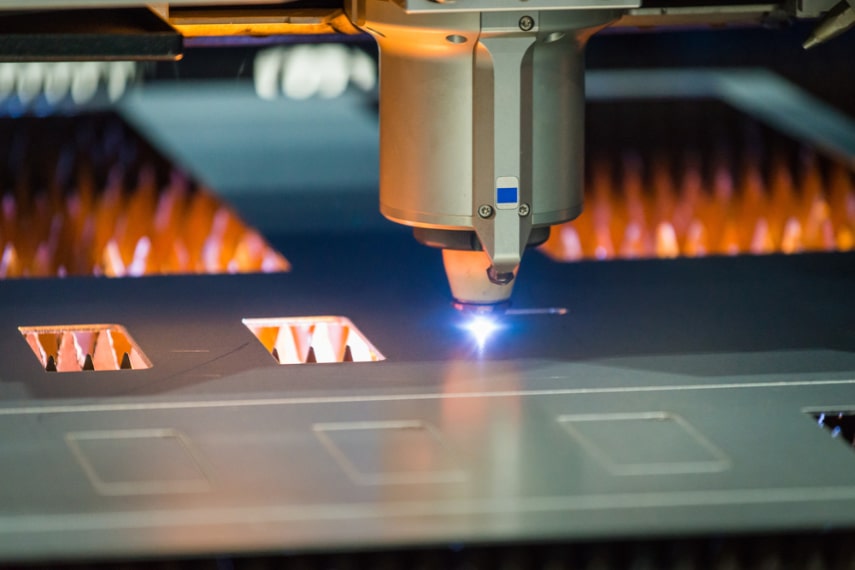
Laser cutting is an efficient and high-precision manufacturing method which uses a laser cutter to cut and etch into a material; laser cutting is often chosen as a cutting method by manufacturers for its reliability, speed, and energy efficiency.
What is the laser cutting process?
The laser cutting process begins with product design; once agreed upon, the design can then be programmed into the CNC laser cutter using digital software – this controls the behaviour of the laser cutter.
A laser resonator produces an intense and concentrated beam of light which is focused towards the surface of the material to be cut. Depending on the laser cutting equipment and method, the laser will melt, burn or evaporate the material to form a cut.
The laser head is able to move above the workpiece with an XY gantry which guides its movements forwards and backwards, and from side to side, according to the design to make cuts.
Types of Laser Cutters
The type of industrial laser offers differing intensities based on material thickness and type; these factors are critical in achieving a high-quality laser cutting finish, so selecting the right type is crucial.
Carbon dioxide lasers are one of the most common types of laser cutters; they’re a lower intensity laser, suitable for sheet metal laser cutting, offering a smooth surface finish with little need for linishing.
Neodymium lasers, made from neodymium-doped crystals, produce a higher intensity laser suitable for materials which require higher amounts of energy to metal and are used for etching, marking or even welding steel.
Fibre lasers are made from a seed laser and amplified using fibreglass for a highly accurate beam of light. The technology of the fibre can cut yellow steels such as brass and & copper as well as marking and etching the steel. It is programmed similar to that of the CO2 laser using Cadcam and similar software technology and has the advantage of offering a very small tolerance together with a smooth finish.
Cutting Methods
As mentioned above, there are several methods of laser cutting which should be chosen depending on the requirements of the project.
- Fusion cutting. Fusion cutting uses an inert gas (such as nitrogen) to blow partially-melted material from the kerf (or cut).
- Flame cutting. Oxygen is used as the assist gas in flame cutting, which reacts with the material when it is blown into the kerf to burn the material away.
- Remote cutting. The laser evaporates the material without help of an assist gas – this is used for thinner and more delicate materials.
- Fibre laser cutting. Fibre Laser Cutting technology works by focusing the power of a high-power laser beam. The advantage of fiber lasers over other types of lasers is that the laser light is both generated and delivered by an inherently flexible medium, which allows easier delivery to the focusing location and target.
Industries That Use Laser Cutting
In many industries, laser cutting is a key piece of machinery that transforms production processes and boosts efficiency.
The construction industry relies on laser cutting for structural components, providing speed and precision for major steel projects. It facilitates the fabrication of complex structural elements, reducing manual labour and construction time.
In the electronics sector, laser cutting is widely used for cutting delicate components with precise measurements and intricate designs.
Likewise, in the medical equipment industry, laser cutting is essential for fabricating complex medical components with precision and accuracy.
Laser Cutting Advantages
Laser cutting offers many advantages, including unmatched precision and speed in fabricating intricate metal parts. With laser technology, you can achieve unparalleled accuracy by focusing the laser beam to create detailed and complex shapes with ease.
The versatility of laser cutting allows you to work with various materials, particularly metals.
Additionally, laser cutting's high speed is well-suited for large projects that require timely completion, allowing for fast turnaround times while maintaining high quality.
Materials Suitable For Laser Cutting
When considering materials suitable for laser cutting, a wide range of options are available, each with specific characteristics and requirements.
- Metal, laser cutters can cut mild steel, stainless steel, and non-ferrous metals.
- Acrylic, a transparent plastic known for its strength and optical clarity, requires ventilation and recommended lasers to avoid scorching.
- Plywood, made from wood veneers, needs ventilation and higher blower pressure for cleaner cuts, with fast speeds potentially affecting kerf size.
- Medium Density Fiberboard (MDF), is challenging to cut and demands high power and blower pressure.
- Cardboard, a low-cost option, requires ventilation, moderate power levels, fast feed speeds, and low blower pressure.
Each material presents unique challenges and benefits, making it important to choose the right one based on your project's needs and the capabilities of your laser cutter.
Click here to find out more, alternatively contact us by calling or emailing us and our specialist experts can help you.

How can we help?
With over 17+ years of knowledge and experience, we’re confident we can offer a flexible solution beneficial to both parties, get in touch with us today.